Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Beijing National Research Center for Information Science and Technology (BNRist), Beijing Innovation Center for Future Chips, Department of Electronic Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Functional Materials for Informatics, Shanghai Institute of Microsystem and Information Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 200050, China
3 Frontier Science Center for Quantum Information, Beijing, 100084, China
4 Beijing Academy of Quantum Information Sciences, Beijing, 100193, China
Quantum key distribution (QKD) would play an important role in future information technologies due to its theoretically proven security based on the laws of quantum mechanics. How to realize QKDs among multiple users in an effective and simple way is crucial for its real applications in communication networks. In this work, we propose and demonstrate a fully connected QKD network without trusted node for a large number of users. Using flexible wavelength division multiplexing/demultiplexing and space division multiplexing, entanglement resources generated by a broadband energy-time entangled quantum light source are distributed to 40 users. Any two users share a part of entanglement resources, by which QKD is established between them. As a result, it realizes a fully connected network with 40 users and 780 QKD links. The performance of this network architecture is also discussed theoretically, showing its potential on developing quantum communication networks with large user numbers owing to its simplicity, scalability, and high efficiency.
华北电力大学 电气与电子工程学院, 河北 保定 071003
提出了一种具有双模大模场面积的多芯光纤,建立了该多芯光纤的电磁场模型并采用有限元方法对其进行求解。基于该模型研究了光纤的模式特性和弯曲特性,系统分析了纤芯间距、纤芯半径和芯包折射率差对光纤模式特性和基模有效模场面积的影响。结果表明:通过引入空气孔并适当减少纤芯间距、纤芯半径和芯包折射率差,该光纤能实现严格的双模传输。保持双模传输时,通过增大纤芯间距,减小纤芯半径和芯包折射率差均有助于增大基模的模场面积。通过调整结构参数,在近似满足双模传输的条件下,光纤的基模模场面积在平直状态下可达到3155μm2。
多芯光纤 双模 大模场面积 弯曲损耗 multicore fiber dualmode largemodearea bending loss
华北电力大学 电气与电子工程学院,河北 保定 071003
针对多模光纤的分布式传感系统受多模光纤布里渊散射特性的影响,利用有限元仿真得到多模光纤6种典型传输模式的电场分布,并从布里渊频移、线宽、峰值增益和布里渊散射谱4个方面仿真研究了单一模式和模式叠加情况下多模光纤的布里渊散射特性。仿真结果表明: 多模光纤不同传输模式的线宽和增益峰值都随着模式阶数的增加略有减少,布里渊频移随模式阶数减小而明显增加;在不受应变和温度影响的情况下,多模式叠加后布里渊散射谱相较单一模式线宽发生展宽,增益峰值大幅减小。
多模光纤 布里渊频移 线宽 增益峰值 布里渊散射谱 multimode fiber Brillouin frequency shift linewidth max gain Brillouin scattering spectrum
1 华北电力大学电子与通信工程系, 河北 保定 071003
2 华北电力大学电力工程系, 河北 保定 071003
基于相似匹配方法的布里渊频移提取算法具有无需预设模型、适应性强的优点。为了获得谱信号参数和扫频参数对算法性能的影响,在仅单一因素变化情况下系统研究了布里渊线宽(简称线宽)、信噪比、扫频间隔、扫频范围对布里渊频移提取准确性的影响规律。结果表明:频移误差与线宽成线性关系,探测谱与参考谱线宽差距本身对算法准确性产生的影响较小;频移误差随参考谱和探测谱信噪比的增加均呈指数规律减小;扫频间隔不变时随参考谱扫频范围增加频移误差存在增加的趋势,同时计算时间线性增加;探测谱的扫频范围为2倍线宽时频移误差最小。研究结果可为布里渊频移的准确提取提供参考。
光纤光学 光纤分布式传感 布里渊散射 布里渊频移 相似匹配方法 影响因素
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Functional Materials for Informatics, Shanghai Institute of Microsystem and Information Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), Shanghai 200050, China
2 CAS Center for Excellence in Superconducting Electronics, Shanghai 200050, China
3 Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
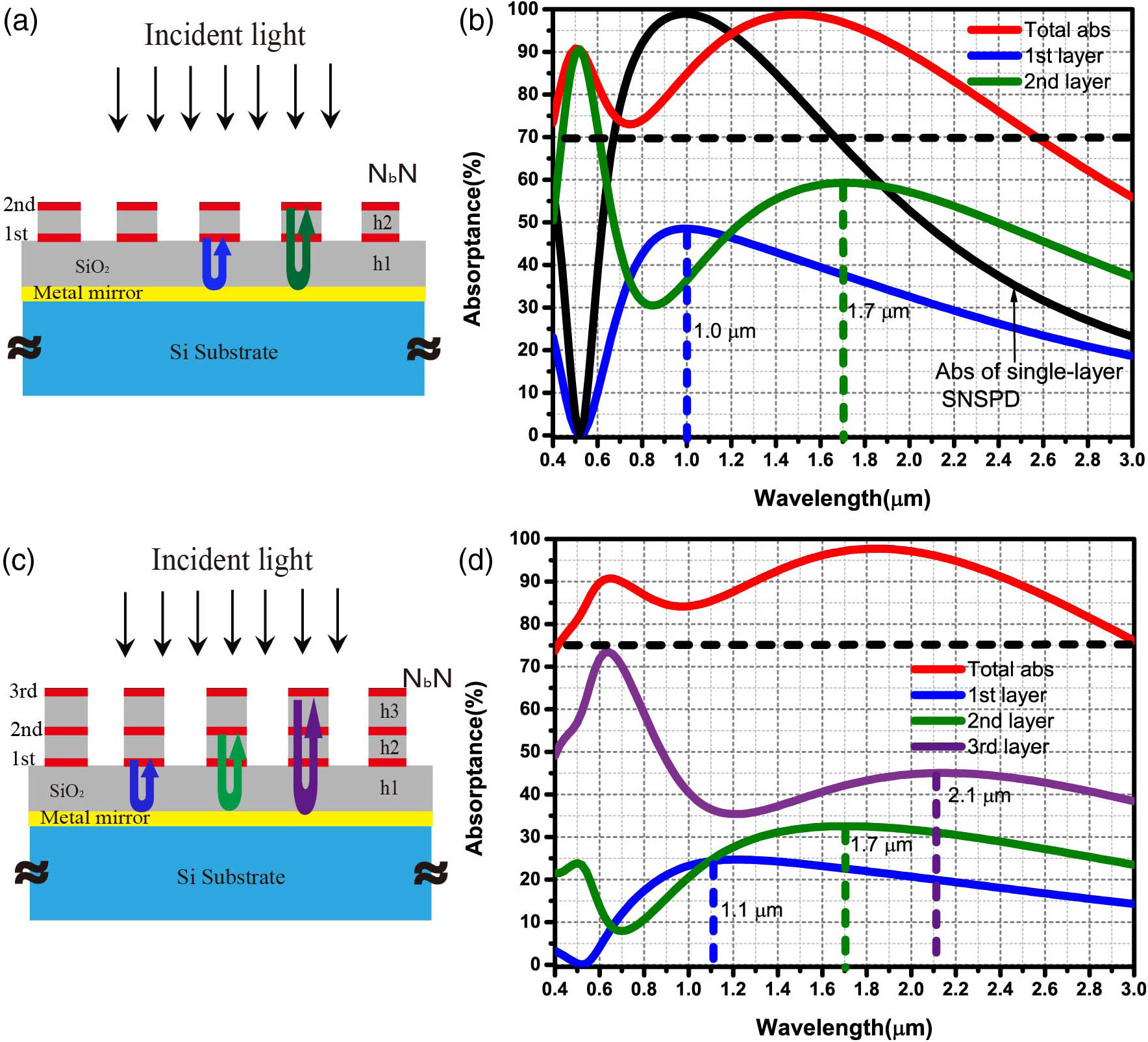
High-efficiency superconducting nanowire single-photon detectors (SNSPDs), which have numerous applications in quantum information systems, function by using the optical cavity and the ultrasensitive photon response of their ultra-thin superconducting nanowires. However, the wideband response of superconducting nanowires is limited due to the resonance of the traditional optical cavity. Here, we report on a supercontinuum SNSPD that can efficiently detect single photons over an ultra-broad spectral range from visible to mid-infrared light. Our detection approach relies on using multiple cavities with well-separated absorbed resonances formed by fabricating multilayer superconducting nanowires on metallic mirrors with silica acting as spacer layers. Thus, we are able to extend the absorption spectral bandwidth while maintaining considerable efficiency, as opposed to a conventional single-layer SNSPD. Our calculations show that the proposed supercontinuum SNSPD exhibits an extended absorption bandwidth with increased nanowire layers. Its absorption efficiency is greater than 70% over the entire range from 400 to 2500 nm (or 400 to 3000 nm), when using two-layer (or three-layer) nanowires. As a proof of principle, the SNSPD with bilayer nanowires is fabricated based on the proposed detector architecture with simplified geometrical parameters. The detector achieves broadband detection efficiency over 60% from 950 to 1650 nm. This type of detector may replace multiple narrow band detectors in a system and find uses in the emerging and rapidly advancing field of atomic and molecular broadband spectroscopy.
Photonics Research
2019, 7(12): 12001425





